There is a certain fulfillment and joy that comes when a woman carries a pregnancy for 38 to 42 weeks period and at the end of the day, give birth to a healthy baby or set of babies. Imagine finding out that your baby has a disease that you have never heard about just after giving birth to them or a few weeks after. I am quite sure that no one wishes for that scenario, but in reality, thousands of rare diseases affect children, and some are not known until after a while when the baby begins to show rather strange abnormalities.
One of such rare abnormalities stem from 8p chromosome, also known as chromosome 8, monosony 8p and a host of other names. Chromosome 8p is a rare genetic condition that affects approximately 350 patients worldwide. This disorder does not affect only one organ but affects every cell, organ, and the whole system.
Just to refreshen our memories a bit or for the sake of those that are not science oriented, a chromosome is a long molecule of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) that contains parts, or all, the genetic information or material of an organism. The chromosome is found in the cell nucleus and is made up of histone/non-histone proteins and RNA (ribonucleic acid) in addition to the DNA. The components of the chromosome makes it very important in passing specific characteristics or information from parents to offspring and across different generations.
Under normal circumstances, every human should have 23 pairs of chromosomes which make up 46 chromosomes in total. The 23 pairs of chromosomes come from two parents who each contribute one pair. Chromosome 8 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, and as I have established earlier, people normally have two copies of every chromosome.
Due to the important function of passing traits across generation, it is equally important that the chromosome is inherited whole from their parents. Any form of alteration might lead to terrible consequences in the offspring. For example, imagine that the information needed for the formation of head in a developing embryo is not completely passed during fertilization, it simply means that the baby will be formed with half-head. What an horrible sight that would be!
When a small, yet unpredictable amount of genetic material from one of the body's 46 chromosomes – chromosome 8 – is missing from the cells, it's called an 8p deletion. For healthy development, chromosomes should have just the right amount of information – not too much, not too little. The wrong amount of material, like most other chromosome disorders, increases the risk of birth defects, developmental delays, and learning disabilities. However, the issues differ and are highly dependent on the genetic material that is lacking.
Many diseases have been related to chromosome 8, and they are caused by mutations caused by chromosome 8 deletion or multiplication. Monosomy 8p is a disorder that occurs when a portion of the 8 chromosomes is deleted. The range and severity of this rare disease's associated symptoms and findings can vary significantly from case to case. It is common to have developmental delays, mental retardation, and other symptoms in neonates and children.
Other malformations like that of the skull and the face region such as a smaller head, vertical folds in the skin, are common symptoms of this chromosomal abnormality.
Diseases related to chromosome 8
As I have pointed out earlier, there are a couple of diseases related to Chromosome 8. Some of them are:
Duplication syndrome
This is a rare genetic disorder caused by a duplication of a region from human chromosome 8. Most people with this experience speech delay, developmental delay, and mild dimorphism(abnormal facial features) with prominent forehead and arched eyebrows, people with 8p duplication syndrome also suffer congenital heart disease (CHD)
Burkitt lymphoma
This is a type of cancer of the lymphatic system (which is responsible for transporting lymph, a fluid containing infection-fighting white blood cells, throughout the body). The jaw, central nervous system, bowel, kidneys, ovaries, and other organs may be affected by this disease.
Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT)
People with this disease typically have muscle tissue and touch sensation problems throughout the body. It is the most common inherited neurological disorder and it affects approximately one in every 2,500 people globally. This degenerative disease typically manifests itself during adolescence or early adulthood.
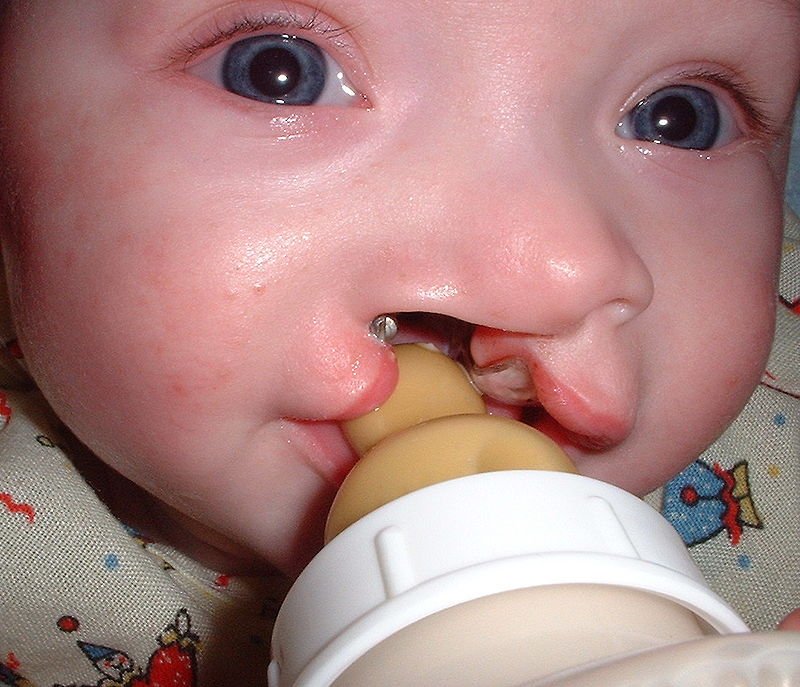
Cleft lip and cleft palate
This is yet another condition involving the lip and palate. A cleft lip is characterized by an opening in the upper lip that extends into the nose. The opening can be on one or both sides, or in the center. When the roof of the mouth has an opening into the nose, this is referred to as a cleft palate. Children with this disorder have feeding difficulties, as well as speech and hearing issues.
Other diseases associated with 8p chromosome worthy to be mentioned include Cohen syndrome, congenital hypothyroidism, Fahr's syndrome among many others.

Can chromosomal abnormalities be diagnosed during pregnancy?
It is recommended to have regular antenatal checks while pregnant. Screening tests and diagnostic tests are available for chromosomal anomalies and other conditions. Screening tests are performed to rule out the possibility of an anomaly. If your baby's screening test results indicate that he or she is at risk for certain chromosomal diseases, a diagnostic test will be recommended. Diagnostic tests detect a wide range of abnormalities, and when they are performed, the results are either negative or positive.
Treatment
There is no treatment or cure for chromosomal abnormalities in many cases. Some interventions, however, may include:
- Genetic counseling
- Occupational therapy.
- Physical therapy.
- Cardiovascular medicines.
More research is still ongoing to help come up with beneficial treatment for this condition.
Thank you all for reading.
References
Originally posted here: https://hive.blog/hive-196387/@hadji/chromosome-8-abnormalities
No comments:
Post a Comment