https://images.hive.blog/768x0/https://www.swisscoat.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/myopia_man-1-800x480.jpg

[src](https://www.swisscoat.com/high-myopia-is-a-risk-factors-of-various-eye-diseases/) If you've been wearing glasses for some time now, you've likely lost hope of any improvement: It seems like every time you visit the optometrist, your eyesight gets worse! *Before we continue, please note that I am not a doctor. I've gained this knowledge from reading. And so, may be wrong on some matters. Corrections via comments welcome!* ## Your eyes are doing their job As with most muscles in your body, your eyes respond to **stimulus**, which in this case, is your *vision*. > Our eyes make small, subconscious adjustments when we look at something. This is done for one reason only: To adapt to your vision so things are clearer When you focus intently at something close-up (like a phone) for some time, your eyes go "hey, let me adjust myself so I can see this phone clearer. #### Making close-up objects clearer will also make far-away objects more blurry ## A look at the eye
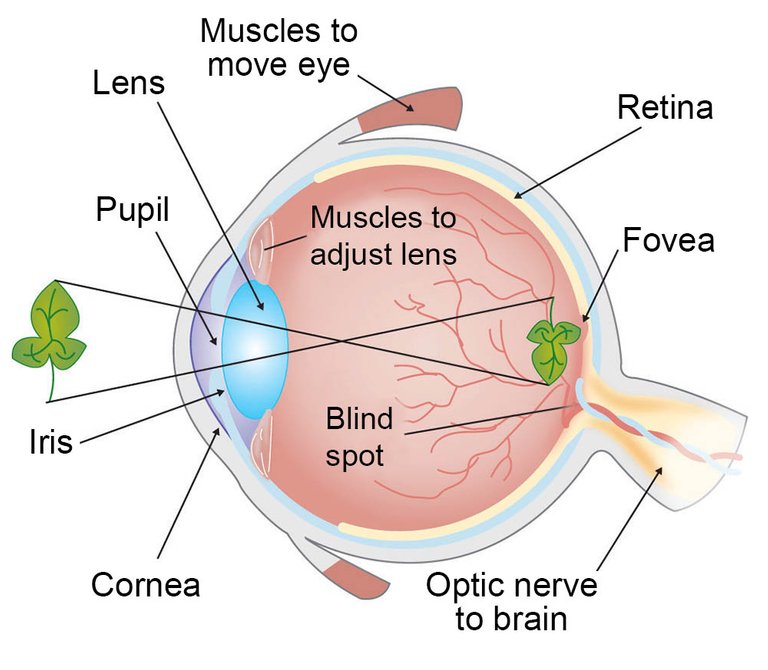
[src](http://askabiologist.asu.edu/sites/default/files/resources/articles/seecolor/eye-anatomy-1000.jpg) The muscles responsible for adjusting lenses and focusing on objects are called your **ciliary muscles**. You can actually *feel* them if you focus hard on something. > When you look at some thing far away, your ciliary muscles **relax**. When you look at something up-close, your ciliary muscles **contract**. ## The elongation of the eye
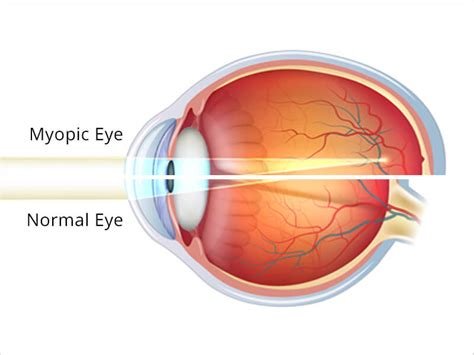
[src](https://www.managemyopia.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/myopia_normal_eye.jpg) After focusing on something close for a long time, your ciliary muscles get tired, just like your hands would if you clenched them for too long. > Here's the problem: Once your eyes "realize" that you'll be doing mostly close up activities, they **elongate themselves** so that the ciliary muscles don't need to contract to see nearby objects. This is bad, now you need glasses to see far away objects! You go to the doctor, and they give you lenses to make *far away* objects clear. After a month of using the phone with those glasses on, you realize that they've somehow 'lost their power' and that you need a stronger prescription. ## Behold, the cycle! Your story is awful similar to the one above. Indeed, mine is too. As you've probably guessed, *your glasses are increasing your myopia instead of fixing it*. ## The eye adapts both ways Think about it, your eye strains to see something nearby, it elongates itself. The reverse is also true: If your ciliary muscles have to strain **a slight bit** to see something far away, it will shorten itself to make it easier for the muscle. Why a slight bit? Well, if your muscles have to strain *too much* to see far away objects, they'll just give up; there goes your chance! # Steps to reverse myopia ## 0. Find a willing optometrist You'll need an optometrist that's willing to help you, mostly with giving you custom-power lenses. ## 1. Have two glasses Have two glasses: A and B. * When reading or doing computer work, you don't *need* to wear full power lenses. If you do, you'll get more of that eye-elongation we saw a minute ago. * Your close-up lens, ie. *A* should be the bare minimum you need to see things clearly. In fact, if it's possible to see clearly without glasses, ditch them. * Your distance lens, ie. *B* should be slightly **less**† than the diagnosed power for your eyes. The rationale is simple: If your eyes have to strain **very very slightly** to see far away objects, they'll 'decide' that it's just easier to shorten your eyeballs. * Don't go overboard with the number of glasses, **two is the maximum**. Otherwise you risk getting a headache from constantly changing focal planes. † 'less' here is relative. If your current prescription > 3D, get a prescription that lower by 0.5D, else get one lower by 0.25D. ## 2. Rest your eyes Constant close up without rest *will* lock up your ciliary muscles. This is called a [ciliary spasm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spasm_of_accommodation) and is bad because it makes the next step useless. Even if you follow all other steps correctly, you are not likely to see any gains if you don't rest your eyes enough. I like to use [Workrave](https://workrave.org/) to remind me to take a break. Set the short break reminder to 15 minutes and you're golden. When on your break, look outside or anywhere that's further than 20 feet (6 metres) for 30 seconds. This will allow your ciliary muscles to *relax* after suffering under all that close-up strain. ## 3. Active focus The concept of active focus can be best understood through [Jake Steiner's write-ups](https://endmyopia.org/active-focus-links/).

[src](https://endmyopia.org/active-focus-visually-explained/) Essentially, active focus is that point where an otherwise blurry object seems clear because of intent focusing. It's important you practice this regularly because it helps with shortening your eyeballs. Wear your *B* glasses, go out and look at signs and license plates. They'll be slightly blurry; try to make them clear and hold it. This takes some time to master and if you're stuck, back to Jake's blog for tips! ## 4. Lighting plays an important role Working in poor lighting is asking for bad eyesight. Harsh lighting has a bad rep for vision-induced headaches. Work in good lighting conditions such as sunlight from a window. ## 5. Nutrition Vitamin A is very important for keeping your eyes healthy. Some vitamin A-rich foods are: * Beef Liver — 713% DV per serving (1 slice) * Lamb Liver — 236% DV per serving (1 slice) * Sweet Potato (cooked) — 204% DV per serving (1 cup) * Kale (cooked) — 98% DV per serving (1 cup) * Carrot (cooked) — 44% DV per serving (1 medium carrot) Eat these! (But don't overdo it on the livers) ## Has it helped? It sure has. It's been just under a year since me doing all the things above, the results have been fantastic: I've managed to reduce 0.75D from my right eye and 0.25D from my left. ## If you're above forty... This needs more evidence, but [shining a deep red light into your eyes daily for 3 minutes can be good for your eyesight](https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/06/200629120241.htm) ## Finally, if you're newly getting minus lenses... Don't. Unless you are confident it's due to eye disease, getting glasses is guaranteed to screw your eyesight in the future. You're likely experiencing a [ciliary spasm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spasm_of_accommodation), where your ciliary muscles get locked up because of a too much strain. And so, I'd recommend keeping away books, computers and phones for some time, letting your eyes come back to their natural state. Ciliary spasms are NOT permanent and usually clear up in less than a week or two. *** Myopia is not fun, and helping so many people fix what's probably their number one daily nuisance gives me a great deal of pleasure and pride. Thanks for reading till the end! — @rxge

Originally posted here: https://hive.blog/hive-175254/@rxge/if-you-wear-glasses-you-should-read-this






No comments:
Post a Comment