https://files.peakd.com/file/peakd-hive/daniky/UUNotqlU-images201.jpeg
## **Overview** **Shortness of breath,** or **[dyspnea](https://www.healthline.com/health/dyspnea),** is an uncomfortable condition that makes it difficult to fully get air into your lungs. Problems with your heart and lungs can harm your breathing. Some people may experience shortness of breath suddenly for short periods of time while others may experience it over a longer period ranging from one week to years. It have been sometimes difficult to diagnose and treat dyspnea even before the outbreak of covid-19 because there are of many different varieties and causes which is one of the reason for writing this article for our understanding on the nature, structure, type cause, symptoms, diagnosis and the treatment of dyspnea and its preventive measures. Kindly follow me as i proceed.

**
[source](https://factdr.com/health-conditions/dyspnea/)
** Dyspnea can happen as a result of overexertion, spending time at high altitude, or as a symptom of a range of conditions. It is a common problem. According to the Cleveland Clinic Center for Continuing Education, "1 in every 4 people who visit the doctor have dyspnea". #### **
**Misconceptions about dyspnea sometimes attributed to Covid 19 as cause of Breathing problem**
**
**
[source](https://www.ccjm.org/content/early/2020/05/12/ccjm.87a.20047)
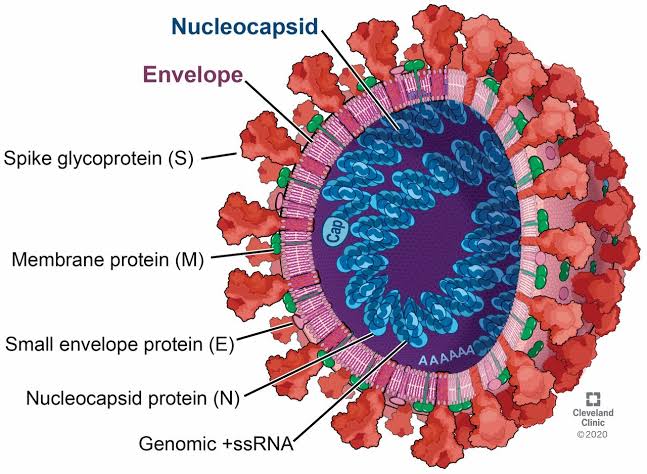
** As COVID-19 pandemic has taken over the lead amidst other viral diseases today, shortness of breath or dyspnea has become widely associated with this illness. But from my analysis, you'll discover that not only covid19 careers are those with breathing difficulties or dyspnea. Some other non covid patients also suffer short term or longterm breathing difficulties due to one cause or the other ranging from allergies, obesity, sedentary life styles, cold weather and others. Many non covid-19 patients have been mistagged as careers of covid-19, making life more miserable for them.

**
[source](https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-yellow-protective-suit-3951373/)
** Covid-19 is now rated one of the most contagious and deadly virus in human history and it's a chronic type of dyspnea whose viral and pathogenic activity has given more insight for research and discovery to its nature, structure and pathological function in science and medicine for better ways of finding the mean to curtail the spread and eradicate the virus. #### **Symptoms of Dyspnea** According to Dr. Steven Wahls, "the most common causes of dyspnea or breathing difficulties include asthma, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), interstitial lung disease, pneumonia, and psychogenic problems that are usually linked to anxiety". Moreover, If shortness of breath starts suddenly, it is said to be an acute case of dyspnea **[¶](https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/314963)**. Other Signs that a person is experiencing dyspnea include shortness of breath after exertion or due to a medical condition,tightness in the chest, feeling smothered or suffocated due to breathing difficulties, rapid, shallow breathing, heart palpitations, wheezing, coughing and labored breathing. If dyspnea occurs suddenly or if symptoms are severe, it may be a sign of a serious medical condition. #### **Causes** An episode of dyspnea is not always directly related to an individual’s health. A person can feel short of breath after intense exercise, when traveling to a high altitude, or going through major temperature changes. However, dyspnea usually relates to health problems. Sometimes, it is just a case of being out of shape, and exercise can improve symptoms. But dyspnea can be a sign of a serious health issue. If shortness of breath starts suddenly, it is called an acute case of dyspnea. **(i). Acute dyspnea** could be due to asthma, anemia, anxiety, pneumonia, allergic, heart failure, reactions, choking on or inhaling something that blocks breathing passageways, serious loss of blood resulting in anemia, exposure to dangerous levels of carbon monoxide, hypotension-which is low blood pressure, pulmonary embolism, which is a blood clot in an artery to the lung collapsed lung, hiatal hernia. Dyspnea is also common among people with a terminal illness. If a person experiences shortness of breath for over a month, the condition is called chronic dyspnea. **(ii). Chronic dyspnea** could be due to asthma, COPD, heart problems, obesity, interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, a disease that causes scarring of the lung tissues. Some additional lung conditions may also cause shortness of breath which include croup, traumatic lung injury, lung cancer, tuberculosis,pleurisy, an inflammation in the tissues surrounding the lungs, pulmonary edema-when too much fluid collects in the lungs, sarcoidosis- when clusters of inflammatory cells grow in the lungs, pulmonary hypertension-when the blood pressure in the arteries to the lungs rises. **Below, is a table showing the differential diagnosis of chronic dyspnea.**
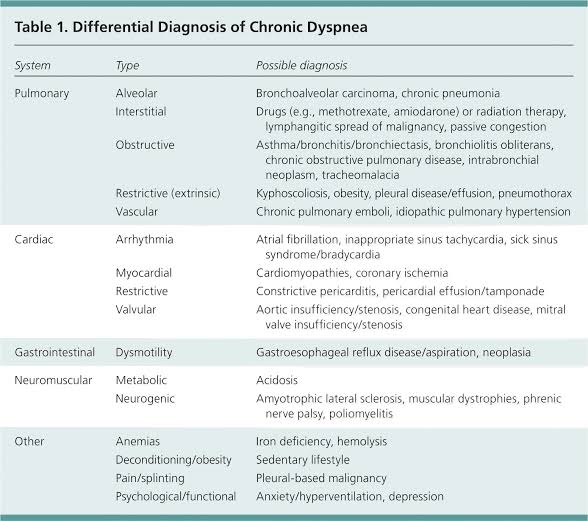
**
[source](https://www.aafp.org/afp/2012/0715/p173.html)
** >#### **Treatment options** The best way to treat dyspnea is usually by treating its underlying cause which can be: >##### **1. Diet and exercise**

**
[source](https://www.pexels.com/photo/strawberries-and-measuring-tape-1172019/)
** eating healthier meals and frequent exercise is one of the ways in treating obesity and a poor fitness level which are the cause of dyspnea you may be experiencing. Go for medical checkup if you have a medical condition that limits your activity level, talk with your doctor about it on how to begin a safe exercise routine to keep your health fit. >##### **2. Pulmonary rehabilitation**
**
[source](https://www.pexels.com/photo/male-massage-therapist-doing-neck-massage-on-patient-4506216/)
** This is a program of supervised exercise and education about breathing techniques to help you overcome lung disease. COPD and other lung problems require the care of a pulmonologist (i.e a doctor who specializes in the health of your lungs and respiratory system). You may as well, need supplemental oxygen in a portable tank to help keep you from feeling out of breath. So this goes a long way in treating dyspnea. >##### **3. Cardiac rehabilitation**
**
[source](https://www.nm.org/healthbeat/healthy-tips/ten-signs-its-time-to-see-a-cardiologist)
** A doctor specializing in heart disorders treats Heart-related causes. These doctor is known as a cardiologist.If you have heart failure, it means your heart is too weak to pump enough oxygenated blood to meet your body’s requirements. Dyspnea is one of several symptoms of heart failure. So, Cardiac rehabilitation can help you manage heart failure and other heart-related conditions. In serious cases of heart failure, an artificial pump may be needed to take over the blood pumping duties of a weakened heart for your survival. >#### **Preventive Measures** To Prevent dyspnea simply means to avoid or managing its many possible causes. The most obvious risk factor for shortness of breath is smoking. If you smoke, seek out a smoking cessation specialist or program in your community. There are many effective products and therapies now that can help you quit smoking. It’s never too late. Within hours of having your last cigarette, your lung and heart health will begin to improve. Breathing problems can also be caused by Air pollution and airborne chemical. So consider using a mask to filter out lung irritants, and make sure your workplace is properly ventilated if you work in an environment with poor air quality. A number of health problems can also be avoided by maintaining a healthy weight. Eat more fresh fruits that are rich in fibre content and avoid saturated foods. Talk to a nutritionist or dietitian to help you plan your meals and change your eating habit. >### **Conclusion** From the above analysis, hope I've been able to give an insight to the symptoms, causes, types, diagnosis and preventive measures of dyspnea. So you can now see the need to take precautionary measures in dealing with shortness of breathe which has led to the death of several millions of victims around the world. It is better to note that Covid-19 is just a fractional part of dyspnea caused by its virus. So there is need for us to unite in combating this ravaging pandemic by following the health guidelines laid down by the World Health Organization (WHO), Center for Disease Control (CDC) and your primary health care provider. Morealso, never hesitate to seek proper medical intervention whenever symptoms of breathlessness persist after taking precautions. Thank you For more details on Dyspnea, kindly go through the references below. **References** 1. **Burki NK.** Dyspnea. Clin Chest Med. 1980;1:47–55. [PubMed](https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7026149/) 2. **Campbell EJM, Howell JBL.** The sensation of breathlessness. Br Med Bull. 1963;19:36–40. [PubMed](https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14018125/) 3. **Carrieri V, Janson-Bjerklie S.** The sensation of dyspnea: a review. Heart and Lung. 1984;13:436–447. [PubMed](https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6376427/) 4. **Fleming PR.** Dyspnoea. In: Hart FD, ed. French's index of differential diagnosis. 12th ed. Bristol: Wright, 1985;216–26. 5. **Ganong WF.** Respiratory adjustments in health and disease. In: Review of medical physiology, 12th ed. Los Altos: Lange Medical Publications, 1985;558–71. 6. [**Mukerji V.** Dyspnea, Orthopnea, and Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea. In: Walker HK, Hall WD, Hurst JW, editors. Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd edition. Boston: Butterworths; 1990. Chapter 11.](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK213/#!po=85.2941) 7. **Rappaport E.** Dyspnea: pathophysiology and differential diagnosis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1971;13:532–45. [PubMed](https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4933005/) 8. **Rees PJ, Clark TJH.** Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea and periodic respiration. Lancet.1979;2:1315–17. [PubMed](https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/92669/) 9. **Seward J, Hayes DL, Smith HC. *et al*.** Platypnea—orthodeoxia: clinical profile, diagnostic workup, management, and report of seven cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1984;59:221–31. [PubMed](https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6708599/) 10. **Zack MB, Pontoppidan H, Kazemi H.** The effect of lateral positions on gas exchange in pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974;110:49–55. [PubMed](https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4834617/) 11. **[Heathline dyspnea](https://www.healthline.com/health/dyspnea#prevention)** 12. **[Medicalnewstoday](https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/314963)**



Originally posted here: https://hive.blog/hive-196387/@daniky/dyspnea-shortness-of-breathe-types-causes-symptoms-diagnosis-treatment-and-preventive-measures









No comments:
Post a Comment