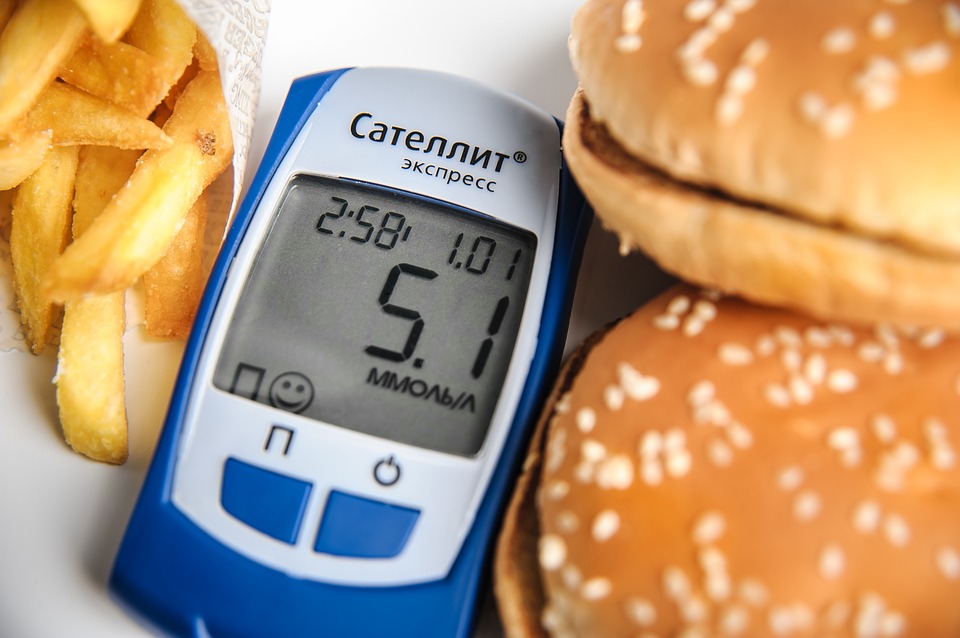
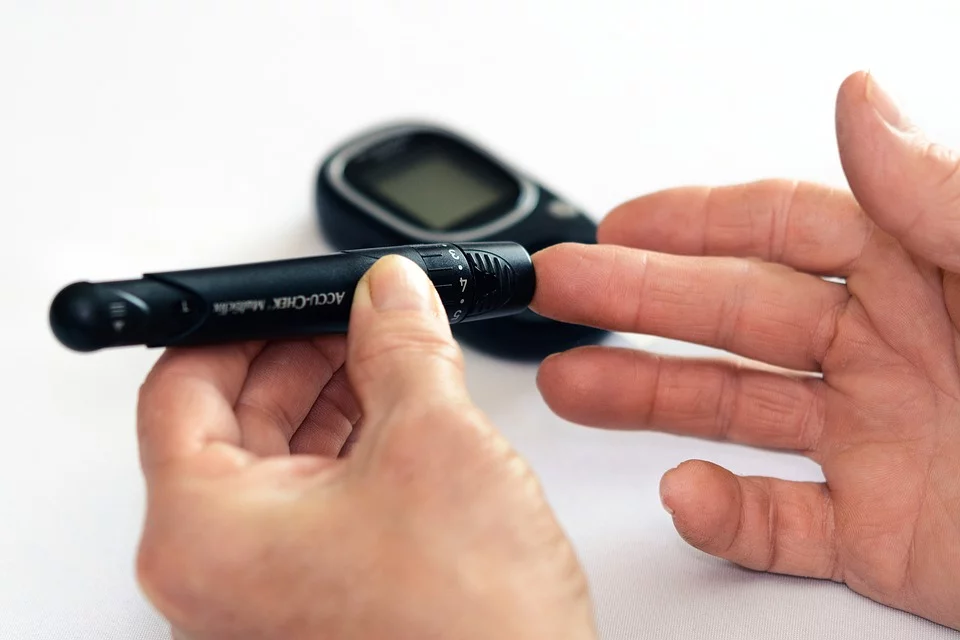
Steemit scientific community receive my greeting, below I present a clinical case of a patient with diabetes mellitus.

.webp)




Originally posted here: https://steemit.com/steemstem/@felixrodriguez/nursing-care-process-1574275695
No comments:
Post a Comment